The Federal Reserve has been aggressive in raising interest rates despite the fact that U.S. inflation is still at multi-decade highs. Rates have really increased by more than two percentage points in only the last six months.In this Article we check on fed interest rate history.
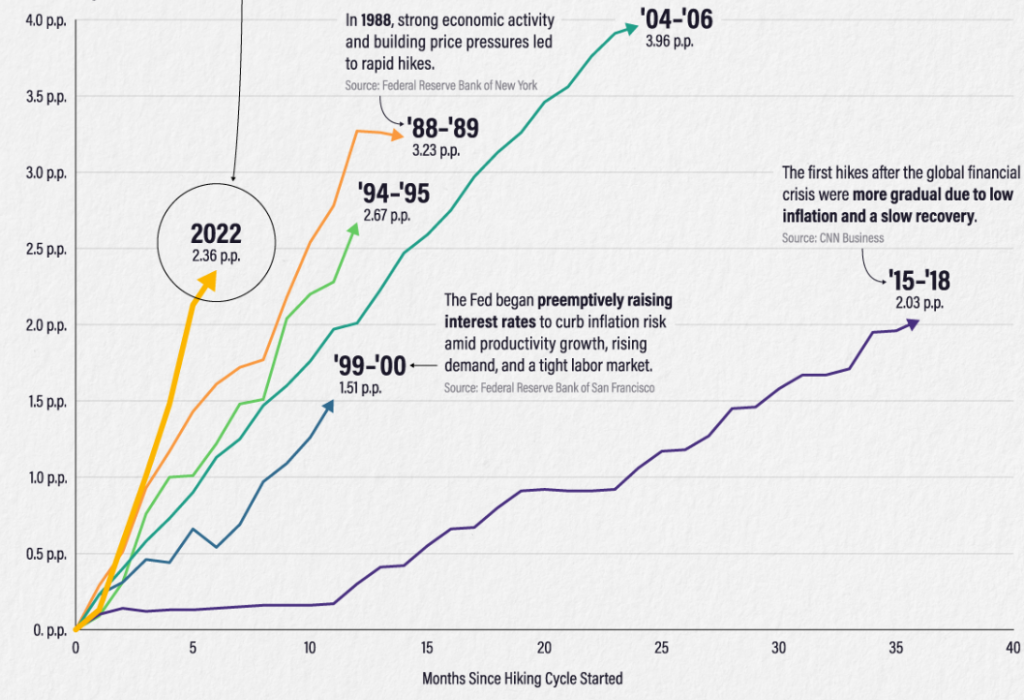
We compared the rate and severity of the current interest rate hikes to earlier periods of monetary tightening over the previous 35 years in this image.
fed interest rate history
Federal reserve Periods of Interest Rate Increases compared :
The weighted average of the interest rates that banks charge each other for overnight loans is what we used to calculate the effective federal funds rate (EFFR). The target range of the Fed has some bearing, but it is ultimately decided by the market. The EFFR in the month of the first rate hike was taken into account as the cycle’s beginning point.
The length and intensity of each cycle of interest rate increases since 1988 are shown here.
| Time Period | Duration (Months) | Total Change in EFFR (Percentage Points) |
|---|---|---|
| Mar 1988 – May 1989 | 14 | 3.23 |
| Feb 1994 – Feb 1995 | 12 | 2.67 |
| Jun 1999 – May 2000 | 11 | 1.51 |
| Jun 2004 – Jun 2006 | 24 | 3.96 |
| Dec 2015 – Dec 2018 | 36 | 2.03 |
| Mar 2022 – Sep 2022 | 6 | 2.36 |
The rate hike cycle from 2022 is the fastest, increasing by 2.36 percentage points almost twice as quickly as the cycle from 1988 to 1989.
On the other hand, the EFFR increased by over four percentage points during the cycle from 2004 to 2006, which saw the most significant interest rate increases. But because the rises were spread out over a two-year period, it took significantly longer to get to this level.
Fed interest rate hike history and timing :
Why are interest rate increases in 2022 so quick? The Fed’s long-term goal of 2% inflation is greatly exceeded by US inflation. In fact, when the rate hikes began in March 2022, inflation was at its highest point in the previous six cycles.
| Time Period | Inflation Rate at Start of Cycle |
|---|---|
| Mar 1988 – May 1989 | 3.60% |
| Feb 1994 – Feb 1995 | 2.06% |
| Jun 1999 – May 2000 | 1.40% |
| Jun 2004 – Jun 2006 | 2.89% |
| Dec 2015 – Dec 2018 | 0.30% |
| Mar 2022 – Sep 2022 | 6.77% |
On the other hand, three rate-hike cycles began with inflation at or below the desired 2% level. When the Fed issued its first rate increase since the global financial crisis in December 2015, inflation was only 0.30%.
The Fed defended its decision to raise rates early by arguing that it can take up to three years or longer for policy decisions to have an impact on the economy. The Federal Reserve (Fed) aimed to prevent future inflationary spikes by gradually boosting rates in the short term.
When we fast-forward to the present, the scene is completely different. Before the Fed started to hike rates, inflation was above the 2% objective for a full year. The Federal Reserve initially thought inflation was “transitory” or short-lived. Currently, inflation is a major source of concern for the economy, and there is a chance that it may have gained enough pace to be challenging to reverse.
Balancing recession and inflation risks:
By the end of 2022, the Fed plans to increase its target rate from its current range of 3-3.25% to roughly 4.4%. They project that inflation won’t reach their 2% goal until 2025, though.
The quick increases in interest rates could trigger a recession in the interim. As other central banks also raise their interest rates, the likelihood of a global recession has increased. The World Bank makes the following recommendations to policymakers to help them prevent a recession:
In order to maintain inflation expectations and, ideally, limit the amount of rate increases required, central banks can convey their policy decisions in plain language.
The development of medium-term spending and tax plans, as well as the provision of targeted assistance to needy households, are all options available to governments.
Through a variety of actions, other economic policymakers can assist in easing supply tensions. For instance, they can implement laws to boost international commerce networks, expand labor force participation, and implement energy conservation measures.
Fed interest rate history
based on : Annual %change, Average Yield , Year Open ,Year High ,Year Low and Year Close rates
Do check out our chart section we post daily interesting charts.





